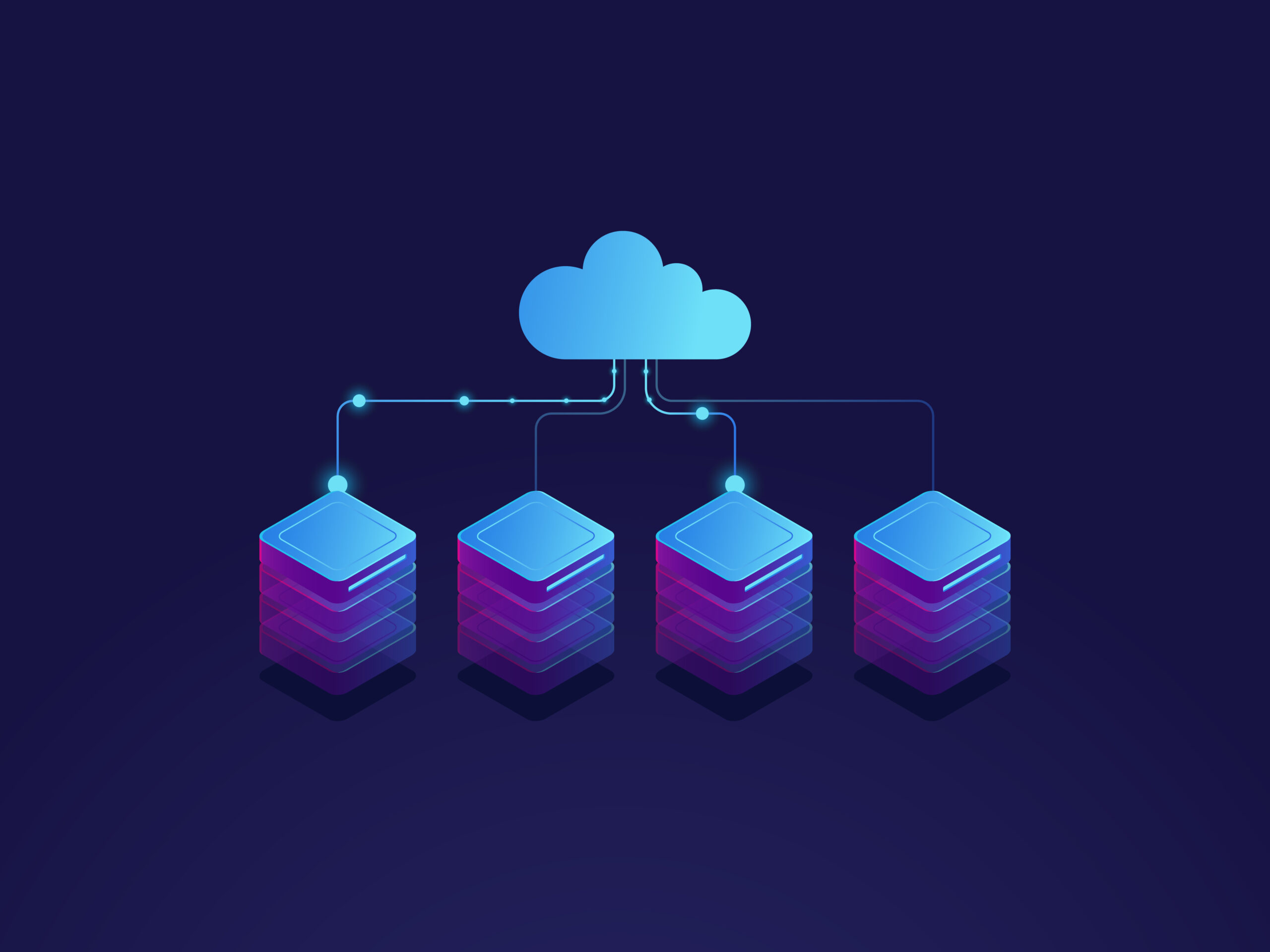
Cloud scalability refers to a system’s ability to handle increasing workloads by adjusting its resources—such as processing power, storage, and memory—on demand. It is a core advantage of cloud computing, allowing businesses to grow without facing performance issues or overprovisioning costs.
There are two main types of scalability: vertical and horizontal. Vertical scaling (scaling up) involves adding more power to an existing machine, while horizontal scaling (scaling out) means adding more machines or servers to handle the load.
Scalability is especially important for startups, e-commerce platforms, or any company expecting rapid growth or seasonal traffic spikes. With scalable cloud infrastructure, organizations pay only for the resources they use, leading to greater efficiency and cost savings.
Key cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer auto-scaling features, which automatically adjust resources based on real-time demand.
Understanding cloud scalability helps in planning infrastructure, improving user experience, and ensuring system reliability. Businesses that leverage scalable solutions are more agile, competitive, and ready to meet changing market demands.